Speed Run DL
In this speed run tutorial, we'll be writing a contract to send/receive messages between chains. This is a code along tutorial, you can copy the code snippets into Remix or the dev environment of your choice. In case you are stuck, you can take peak at the entire code on GitHub. We'll be highlighting key functions and what they do throughout the tutorial. Some configuration variables have been hardcoded in the example.
We'll be deploying the same copy of the contract on Goerli and Mumbai testnet and sending the message "Hello World" from Goerli to Mumbai. You can also deploy it on any supported networks. Let's get started!
Step 1 : Boilerplate code
Below is the boilerplate code needed to get started. ISocket is the interface used by our contract to interact with Socket.
Hello World is the contract which we'll be writing to send/receive messages.
// SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-3.0
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
interface ISocket {
function outbound(
uint32 remoteChainSlug_,
uint256 minMsgGasLimit_,
bytes32 executionParams_,
bytes32 transmissionParams_,
bytes calldata payload_
) external payable returns (bytes32 msgId);
function connect(
uint32 siblingChainSlug_,
address siblingPlug_,
address inboundSwitchboard_,
address outboundSwitchboard_
) external;
function getMinFees(
uint256 minMsgGasLimit_,
uint256 payloadSize_,
bytes32 executionParams_,
bytes32 transmissionParams_,
uint32 remoteChainSlug_,
address plug_
) external view returns (uint256 totalFees);
}
contract HelloWorld {
}
Step 2 : Initialise state variables, events, modifiers
State variables
message is the message which will be set on the remote plug
destGasLimit is the gas limit of setting the message on the destination chain, this value varies depending on the chain.
You can learn more about the other variables in Configuring Plugs
Events
MessageSent is emitted when a message is sent from the source plug and MessageReceived is emitted when the message is received on the destination plug.
string public message = "Hello World";
address owner;
/**
* @dev Hardcoded values for Goerli
*/
uint256 destGasLimit = 100000; // Gas cost of sending "Hello World" on Mumbai
uint32 public remoteChainSlug = 80001; // Mumbai testnet chain ID
address public socket = 0xe37D028a77B4e6fCb05FC75EBa845752cD62A0AA; // Socket Address on Goerli
address public inboundSwitchboard =
0xd59d596B7C7cB4593F61bbE4A82C1E943C64558D; // FAST Switchboard on Goerli
address public outboundSwitchboard =
0xd59d596B7C7cB4593F61bbE4A82C1E943C64558D; // FAST Switchboard on Goerli
event MessageSent(uint32 destChainSlug, string message);
event MessageReceived(uint32 srcChainSlug, string message);
modifier isOwner() {
require(msg.sender == owner, "Not owner");
_;
}
modifier isSocket() {
require(msg.sender == socket, "Not Socket");
_;
}
error InsufficientFees();
constructor() {
owner = msg.sender;
}
Step 3 : Config Functions
connectPlug function connects our Hello World Plug to its sibling Plug on another chain. This connection is required for the Plugs to send/receive messages from one another.
function connectPlug(address siblingPlug_) external isOwner {
ISocket(socket).connect(
remoteChainSlug,
siblingPlug_,
inboundSwitchboard,
outboundSwitchboard
);
}
Step 4 : Sending messages
sendMessage sends the "Hello World" message to the remote chain. This function calls Socket and initiates the outbound cross-chain message
_getMinimumFees fetches the fees for including messages in Packets & executing them. This can be used to verify sufficient fees are passed when sending the message. You can learn more about this in Fees.
function sendMessage() external payable {
bytes memory payload = abi.encode(message);
uint256 totalFees = _getMinimumFees(destGasLimit, payload.length);
if (msg.value < totalFees) revert InsufficientFees();
ISocket(socket).outbound{value: msg.value}(
remoteChainSlug,
destGasLimit,
bytes32(0),
bytes32(0),
payload
);
emit MessageSent(remoteChainSlug, message);
}
function _getMinimumFees(
uint256 minMsgGasLimit_,
uint256 payloadSize_
) internal view returns (uint256) {
return
ISocket(socket).getMinFees(
minMsgGasLimit_,
payloadSize_,
bytes32(0),
bytes32(0),
remoteChainSlug,
address(this)
);
}
Step 5 : Receiving Messages
inbound is called by Socket on the destination Plug for executing the message once it's verified. More in this in Lifecycle
_receiveMessage sets the value of the new message and emits the MessageReceived event
function _receiveMessage(
uint32 _srcChainSlug,
string memory _message
) internal {
message = _message;
emit MessageReceived(_srcChainSlug, _message);
}
function inbound(
uint32 srcChainSlug_,
bytes calldata payload_
) external isSocket {
string memory _message = abi.decode(payload_, (string));
_receiveMessage(srcChainSlug_, _message);
}
Step 6 : Deploying contracts
We'll be deploying the same contract on Goerli and Mumbai testnets. However, to make it easier to send our first message, we've hardcoded some configuration variables specific to Goerli and Mumbai. Click the links below to deploy each of them
Goerli
🚀 Deploy Goerli contract on Remix
Mumbai
🚀 Deploy Mumbai contract on Remix
You can head over to Remix and compile the code for SpeedRunGoerli
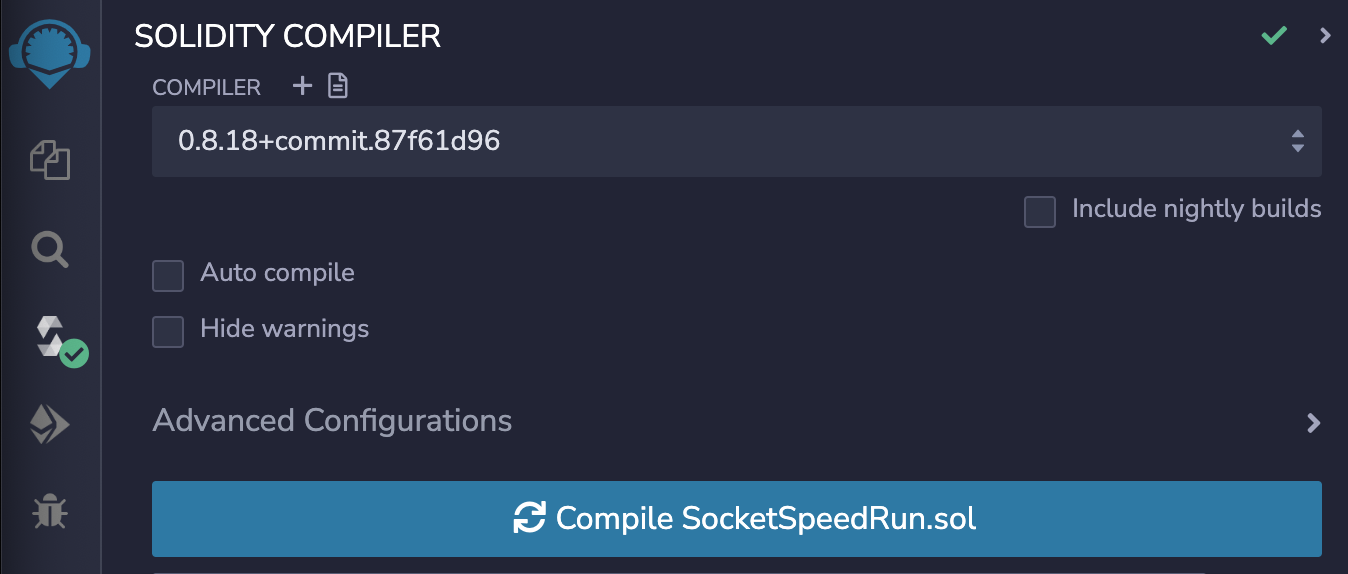
Then, deploy it
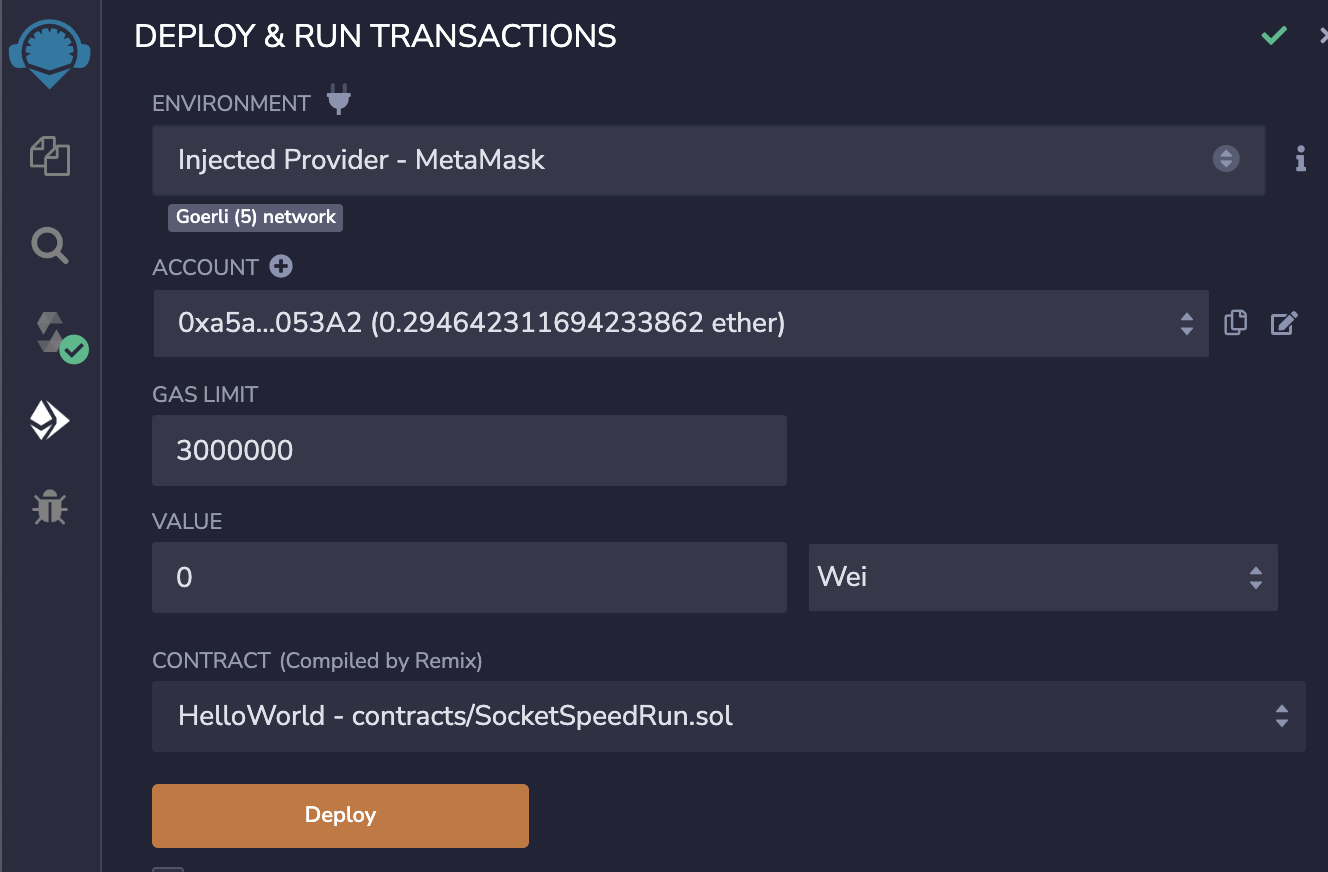
You'll then have to deploy the SpeedRunMumbai contract following the same steps.
Step 7 : Configuration
Once you've deployed the contracts on Goerli and Mumbai, call the connectPlug function with the address of the contract deployed on the other chain. You need to do this on both contracts deployed on respective chains.
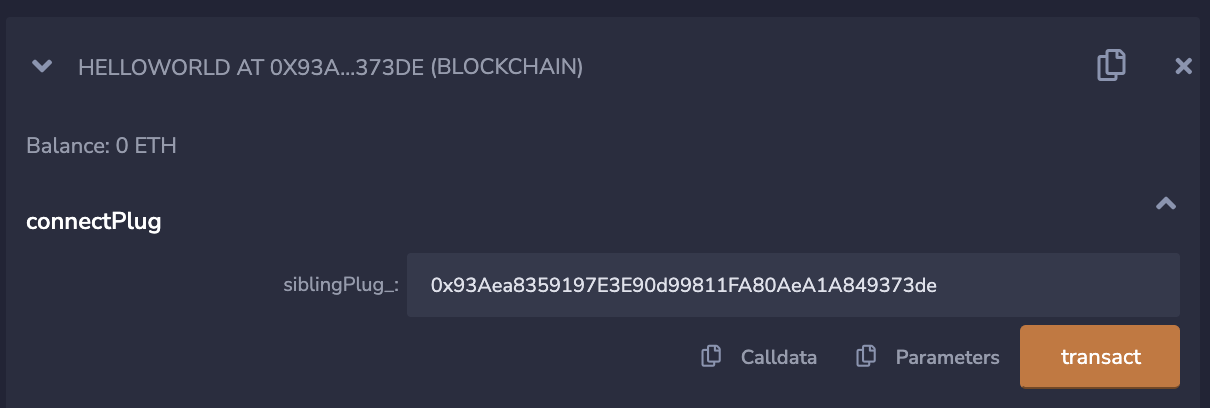
For instance, on Goerli you would call connectPlug with the address of the contract deployed on Mumbai and vice-versa. This establishes a connection between the two Plugs deployed and you can now send messages between them!
Step 8 : Hello World
To send your first message, call the sendMessage function on Goerli. You need to send a fee in ETH as value when calling sendMessage. This fee can be calculated using the Fee Estimate API
You can enter the totalFee returned by this API as value when sending the transaction
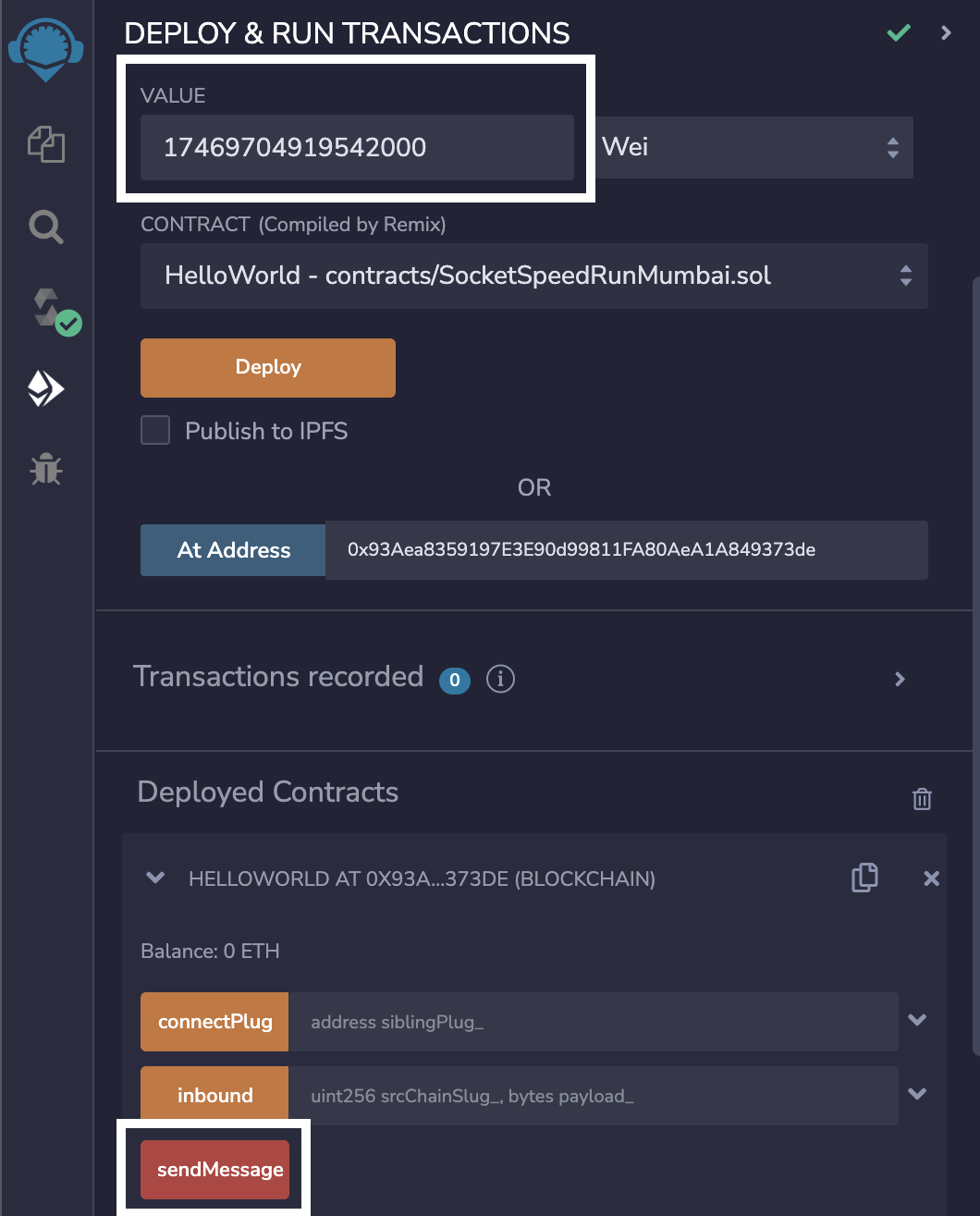
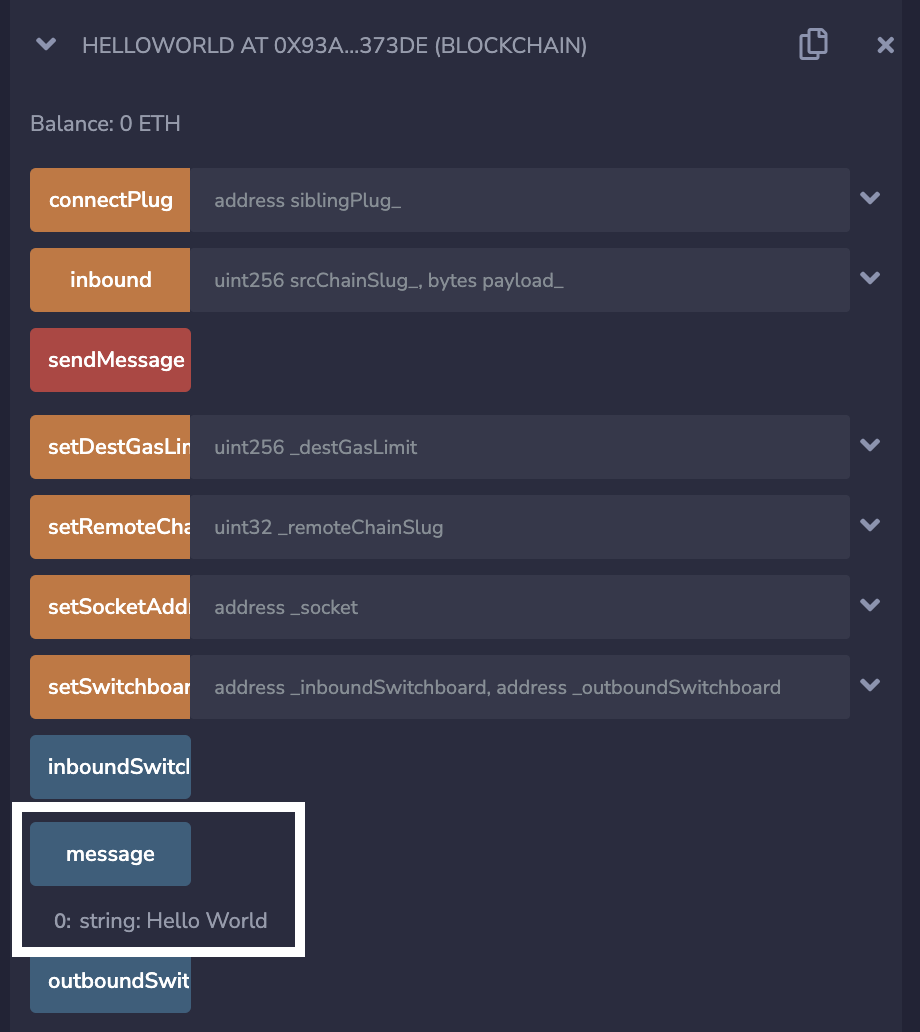
That's it! You can now track the status of your message using the Status Tracking API. Once your message is executed on Mumbai, you'll be able to see the message value set to "Hello World" on Mumbai.