Configuring Plugs
Connecting your cross-chain smart contracts (i.e. Plugs) is as easy as creating a Plug on chain A and chain B, connecting both Plugs to their chain's canonical Socket deployment, and configuring both Plugs to reference one another.
Before getting started on configuring your Plugs, here are a few things to keep in mind:
- Socket allows only Plugs to update this configuration/connection at any point
- Connection should be permissioned at the Plug level by either
owner keys, protocol governance. Or, to make the connection immutable, you can block re-connection forever - Malicious configuration while connecting to Socket could cause unintended actions.
- Connections are pair-wise, i.e you connect PlugA on ChainA to PlugB on ChainB. To extend your deployment to chain C, you would pair a PlugC on ChainC with Plugs on ChainA and ChainB respectively
You can read more about Plugs here. Once connected, you can use the Outbound and Inbound methods to send and receive messages.
Configuring Plug Parameters
Plugs should be deployed on respective chains before they can be connected to their sibling Plugs deployed on other chains. Once you are ready with Plugs deployed on the networks you want to work with, it's time to get Plugged!
Here's the parameters required for connection
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| siblingChainSlug | ChainSlug of the network the sibling plug is deployed on, you can find all chainSlugs here |
| siblingPlug | Address of the plug deployed on the sibling chain |
| inboundSwitchboard | Switchboard address used for receiving messages from siblingPlug |
| outboundSwitchboard | Switchboard address used for sending messages to siblingPlug |
You can find addresses for all verified Switchboards and Socket contracts in Deployments
Connecting your Plugs
Once you have the Socket address you are connecting to, you just need to call the connect method on it to configure your Plug on that chain. Remember, you need to call connect on both the chains you want to work with.
Below is a quick example for how your Plug can call the connect method on Socket
ISocket socket = ISocket(socket_address);
function connectToSocket(
uint32 siblingChainSlug,
address siblingPlug,
address inboundSwitchboard,
address outboundSwitchboard
) external {
// ensure its permissioned
require(msg.sender == AUTHORISED_CONNECTOR, "Caller is not authorised to make make connections");
// finally just call the socket to connect
socket.connect(
siblingChainSlug,
siblingPlug,
inboundSwitchboard,
outboundSwitchboard
);
}
Testing your connection
Once you are done connecting, the transaction will emit a log called PlugConnected
For reference, checkout this example tx of connecting a Plug
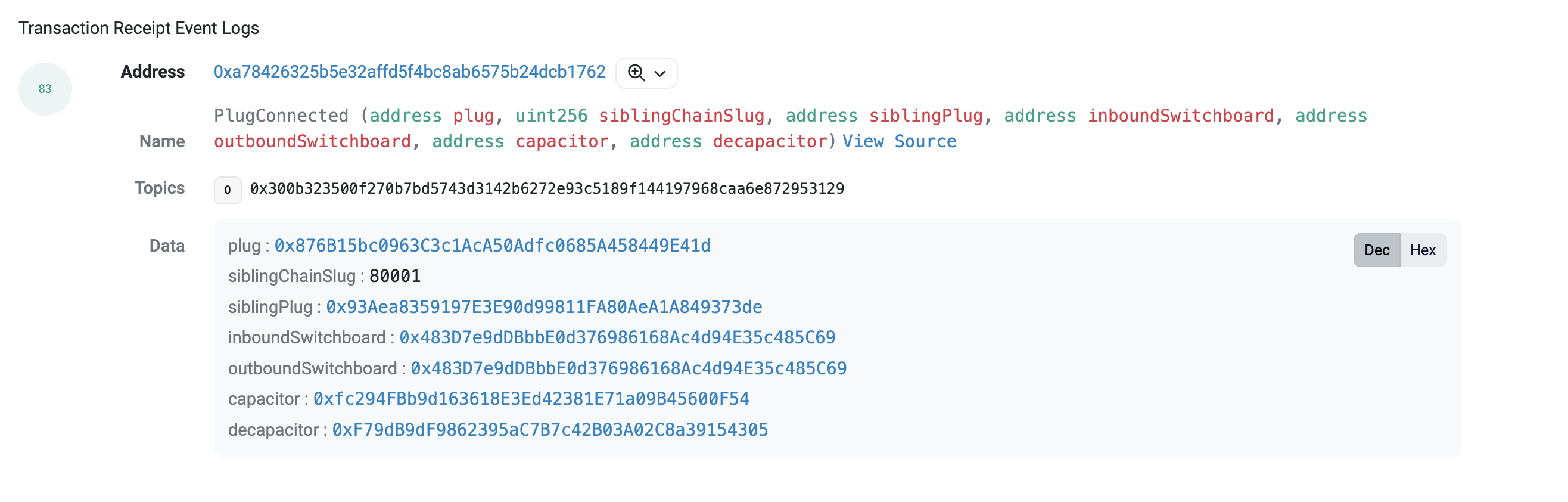
Furthermore, you can do the following to check the connection is successful :
- Call the
getPlugConfigfunction on the Socket contract that returns the config for your Plug for a given destination ChainSlug - Use the Check Connection API that reads the configs and aids you to make sure your connection is correct